Selection criteria for immigrant workers
24 August, 2006
Summary1. The government has toned down its claims that migration brings significant economic benefits to the UK. It now claims only that migrants cause a small but positive increase to gross domestic product per capita.
2. However, if dependent children are taken into account, this small positive increase becomes a small decrease. In other words, the contribution of immigration to the standard of living of the host population is negligible even on the governments calculation, and slightly negative on ours.
3. Successive studies have shown that the economic performance of migrants varies enormously. We calculate that a worker must earn about 27,000 a year to make, on average, a positive contribution to GDP per head and a positive fiscal contribution over their lifetime. This, as it happens, is the average salary for those in full time employment. Only about 20% of the working age migrant population are earning this amount.
4. A similar result would apply to the UK-born population but the difference is, of course, that the government can choose which work-related migrants are allowed to settle in the UK. Accordingly, we suggest that employment-related migration leading to settlement should be restricted to the highly skilled who are filling a vacancy which cannot be filled by EEA citizens and with a salary in excess of the average of 27,000 per year.
5 Skilled migrants from outside the EU should only be allowed into the UK on a temporary basis to provide a short-term solution to labour market gaps while a British worker is trained.
6. As the government acknowledges, there is no reason to bring unskilled migrants to the UK given the large numbers of East European workers available to fill these positions.
Detail
7. Migrationwatch has shown that the governments successive claims that migration gives significant economic benefits to the UK are at best overstated and usually just incorrect (see Annex A for a summary and Migrationwatch briefing papers 1.1 to 1.10 for more detail.)
8. The latest official claim, given by Lord McKenzie of Luton, in response to a question from Lord Lamont was as follows:
Lord Lamont of Lerwick asked Her Majesty's Government:
What studies they have made of the impact of immigration on gross domestic product per capita in the United Kingdom; and what were the results. [HL5379]
Lord McKenzie of Luton:
The Government have a close interest in the economic effect of migration and believe that immigration is broadly positive for the UK, boosting labour market flexibility and economic growth. This view has been endorsed by a recent European Commission report that studied the impact of the accession to the European Union of central and eastern European countries in May 2004.
The latest official statistics (summer 2005) show that around 10 per cent of people above the age of 16 were migrants, defined as people not born in the UK. Migrants typically have lower employment rates than the UK average, around 5 per cent lower, but typically earn 8 per cent more. Assuming that the higher earnings signify that migrants are, on average, more productive, this would indicate that migrants contribute around 11 per cent to total gross domestic product, and cause a small but positive increase to gross domestic product per capita.
9. So, the government has moved from a position where they were talking about migrants making up 8% of the population but contributing 10% to GDP[1] , implying that they were 25% more productive than the UK-born population, to saying that migrants make a small but positive increase to GDP per capita. Migrationwatch has previously shown that the former claim was disingenuous UK-born children of migrants had not been included in the migrant population.
10. It is encouraging, therefore, that the government has moved to a more measured view of the economic performance of migrants. However, even this exaggerates the true contribution because it only looks at the adult population.
11. When earned income is used as a proxy for GDP contribution the effect is that there are two groups of people those who have retired and children under 16 who are classified as contributing little or nothing to GDP, that is they are dependants. Both groups need to be taken into account when measuring GDP per head. Including the retired population in the calculations but excluding children distorts the picture because the migrant population is typically younger than the UK-born population. They therefore have fewer pension age dependants but more dependent children.
12. Migrationwatch has therefore obtained data from the Labour Force Survey to compare GDP per head of the migrant and UK-born populations when dependent children as well as retired people are included in both groups.
The data shows that populations and earnings are as follows[2].
| UK-born | Foreign-born | UK-born percentage |
Foreign-born percentage | |
| 1.Working adults (16+) |
25,544,000 | 2,836,000 | 90% | 10% |
| 2. Non-working adults (16+) |
16,664,000 | 2,142,000 | 88.6% | 11.4% |
| 3. Adults (aged 16+) |
42,208,000 | 4,979,000 | 89.4% | 10.6% |
| 4. Dependent children of above |
9,913,000 | 1,580,000 | 86.3% | 13.7% |
| 5. Total | 52,121,000 | 6,559,000 | 88.8% | 11.2% |
| 6. Percentage of earnings (see para. 13) |
89.1% | 10.9% |
13. On earnings, the data shows that the total earnings of the UK-born and foreign-born adult populations were about 505 billion and 62 billion respectively. By this measure the UK-born and foreign-born therefore contributed 89.1% and 10.9% to GDP respectively (in line with the governments figures of 11% see paragraph 8 above). Our figures also confirm that the governments statement that migrants make up 10.5% of the adult population is also broadly correct. If the adult population only is taken into account migrants do, therefore, contribute slightly more to GDP per head than the UK-born population (l0.9% of earnings compared with 10.6% of the adult population lines 6 and 3 respectively). However, when dependent children are taken into account the position is reversed. That is migrants and their children make up 11.2% of the total population (line 5) but account for just 10.9% of earnings (line 6). Overall, therefore, there is no case for suggesting that immigrants contribute disproportionately to GDP. However, successive studies by the IPPR[3] and the Institute of Fiscal Studies[4] have shown that the economic performance of migrants varies enormously. It is important, therefore, that, where we can, we select only those people who can make a positive contribution to the UKs economy.
14. In determining who makes a positive contribution a clear distinction needs to be made between temporary migrants and migrants who settle in the UK. The former are typically young and single and are unlikely to make significant calls on government services and benefits.
15. Migrants who settle in the UK may, similarly, start by making little or no call on public services and benefits, but later they may be joined by a non-working spouse, start a family and enjoy considerable public benefits such as education. Later when their children have grown up they may again make little call on public services and benefits. Then, when they retire, their call on State services will increase again as they draw a State pension and typically become greater users of services such as the NHS.
16. For migrants who come to the UK to work with the intention of settling it is therefore important to assess their likely contribution over a lifetime not just in the short-term.
17. Economic contribution can be measured in three ways:
| • | Fiscal contribution (would they contribute more in taxes and national insurance than they take out in public services and benefits?) |
| • | GDP contribution (would they contribute more in GDP per head than the average thus effectively raising productivity?) |
| • | Labour market flexibility (do they fill essential positions that cannot be filled from the native workforce?) |
Fiscal contribution
18. We have data readily available for 2003/4 so we have used that year for our calculations.
19. In that year total expenditure on public services and benefits was 459 billion. Total government receipts were 409 billion made up of:
| • | 114.4 billion in income taxes |
| • | 72.5 billion in national insurance contributions and |
| • | 222.1 billion in other taxes (of which the principal ones are customs and excise taxes of 115.7 billion). |
20. To avoid the analysis being skewed by the deficit in that year of 50 billion of expenditure over income, we have assumed that tax receipts from each source would need to rise proportionately i.e. that all taxes would need to rise by about 12% to achieve fiscal neutrality, giving the following:
| • | 128.4 billion in income taxes |
| • | 81.4 billion in national insurance contributions |
| • | 249.3 billion in other taxes |
21. In their analysis of the fiscal contribution of migrants[5] the Home Office apportioned the vast majority of other taxes according to overall population share. This is not ideal clearly the wealthy pay more indirect taxes than the poorer members of Society but we will follow that convention for the sake of simplicity.
22. Labour Force Survey data for 2003/4 showed an adult population of 45.7 million and a working age (16-64) population of 36.9 million people.
23. The working population is roughly the working age population multiplied by their employment rate = 36.9 million * 74.7%[6] = 27.6 million.
24. The tax and national insurance take per worker would therefore need to be in the region of 7,600 (i.e. tax of 128.4 billion plus and national insurance of 81.4 billion divided by 27.6 million workers) for a break even point to be reached. In 2003/4 this would have equated to a gross income of about 21,600 a year (see Annex B). About 31% of all workers earned more than this in 2003/4.
25. We then add a 10% margin to allow for costs of additional infrastructure which result from additional population. This would point to a level of say 24,000 p.a. earnings (at 2003/4 rates) on average for a person to be making a positive fiscal contribution to the economy. The equivalent wage at 2006 rates would be about 27,000 p.a. (allowing 4% p.a. for wage inflation).
GDP calculations
26. In the calendar year 2003 the UKs GDP was 1,099 billion. 613 billion of this amount was compensation of employees.
27. So, apportioning this amount of GDP generated by employment earnings amongst the working population of 27.6 million people gives average earnings per worker of 22,200 a year.
28. Allowing a 10% margin again would point to a level of around 24,500, at 2003 rates, at which a person would make a positive contribution to GDP per capita similar to the fiscal contribution calculation.
Labour market flexibility
29. In principle, temporary gaps in the labour market should be filled by temporary migration. Such migration, provided it is well managed and controlled, should generally be economically positive and could provide the required flexibility and time to enable the gaps in the labour market to be filled by native workers. However, temporary skills gaps are not a reason for permanent migration so it is important that this distinction be maintained in immigration policy.
What proportion of migrants satisfy the earnings criteria?
30. The following graph shows, for the foreign-born population of working age (16-64/65), the number of people in thousands who are unemployed or inactive (i.e. not working and not seeking employment) and the number (of the total population) who are in the earnings bands indicated [7]. Bars to the left of the line are people who are unemployed, inactive or earning at a level which (on average) will be insufficient to cover the costs of State services and benefits. Those to the right of the line are earning 24,000 or more p.a. and will (on average) be making a positive fiscal contribution to the economy. Overall 3.3 million (80%) of the 4.1 million foreign-born of working age do not make a positive fiscal contribution. (Note the 3.3 million will include some full-time students who are not working at all or only working part-time and therefore included in the lower pay brackets. Some 242,000 overseas students were studying at English higher education institutions in 2004/5.[8] Removing students from both totals brings the proportion down to 79%.)
(The results are, again, likely to be similar for the UK-born population since a progressive tax system is always likely to mean that a relatively small percentage of the population is paying a large percentage of the taxes. However, a properly managed immigration policy would allow us to select people to work and settle here who will make a positive contribution, over their lifetimes, to the UKs economy).
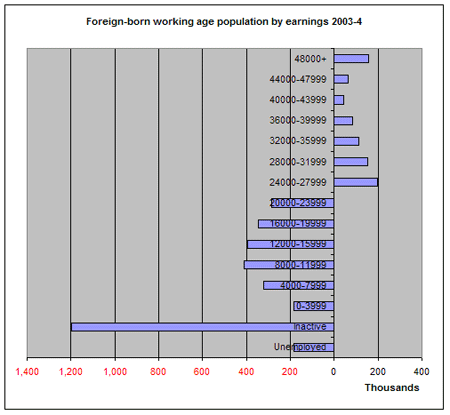
31. Other data shows that it is those with high levels of qualification (NVQ level 4, degree level, and above) who are by far the most likely to satisfy the earnings criteria (In Summer 2005 between 50% and 60% of NVQ 4 qualified migrants were earning 26,000 p.a. or more compared with about 20% of those with NVQ3 (A level).[9] )
Conclusions
32. We conclude that:
| (a) | There needs to be a very clear distinction between people who come to the UK to work here on a temporary basis and those who come to settle. At present (and carried forward into the governments proposed points-based system) all skilled and highly skilled work-related migrants are given the right to apply for settlement after five years in the UK. |
| (b) | Work-related migration leading to settlement from outside the EEA should be primarily restricted to the highly skilled who are filling a vacancy that cannot be filled by an EEA citizen and for a position which carries a salary of at least 27,000 (at current rates). This, in fact, is the average salary for those in full time employment. |
| (c) | If a migrant is applying to come to the UK and settle and wishes to be accompanied by his or her spouse the couple should be considered together. Both would need to have job offers and to have combined earnings of 54,000 p.a. or more. |
| (d) | Work-related migration for the skilled should be restricted to 1) those filling a vacancy which cannot be filled by an EEA citizen and 2) intra-company transfers. All such migrants should be restricted to a maximum stay of 5 years in the UK. Those who wished to settle would have to satisfy the same earnings and qualifications criteria as in (b) above. |
| (e) | Unskilled work-related migration should be restricted to EEA nationals. There is clearly an ample supply of such labour from Eastern Europe. |
Annex A
SEVEN DEADLY SPINS
(The Governments shifting arguments for large-scale immigration)
1. Immigrants are needed to pay our pensions
Dismissed by the Turner Commission on Pensions.
2. 600,000 vacancies need to be filled
Disproved by the facts. Net immigration since 2001 totals 700,000 but vacancies are still at 600,000 (November 2005). The reason is that immigrants fill jobs but also create demand. To argue from vacancies is therefore to advocate an endless cycle of immigration.
3. Immigrants made a net contribution to the budget of 2.5 billion per year in 1999/2000
False. The Home Office study charged the full cost of children of mixed households to the native population. Splitting the cost of these children 50/50 between the two groups results in a net cost to the tax payer of 100 -200 million in that year.
4. Growth would be nearly % lower without net immigration
This was the Prime Minister's claim to the CBI in April 2004. The correct figure is 0.4% but the population is also increased by 0.26% so the benefit per head is 0.14%. This works out at an annual benefit of 2 per week for the average family but even that will decline as immigrants have dependent children and, themselves, grow older. Major studies in the US, Canada and Holland have reached similar conclusions.
5. Immigration provides 15% of trend growth.
Trend growth is about 2.75%. 15% of this is 0.4, so this is the same claim as paragraph 4 above but it is dressed up to look more impressive.
6. Immigrants reduce inflation and interest rates, permitting higher growth
Correct. But immigrants also add to population so the benefit per head to the native population is very small. The latest ITEM Club simulation, addressed only to East European immigration and using the Treasury model, found that 300,000 workers would add 0.8% to GDP after 4 years. On a conservative assumption of half a dependant each, these workers would add 0.75% to the population so the benefit would be only 0.05% of GDP or less than 20 pence per week per head.
However, the main effect is to hold down low wages with the result that that employers and the middle classes benefit while the low paid suffer. Furthermore, it becomes even more difficult to move from welfare to work the 4.2 million British people on unemployment and incapacity benefit.
7a. Immigrants comprise 8% of the workforce but contribute 10% of GDP. Rejected by the Statistics Commission. This takes no account of the higher unemployment among immigrants and the lower participation by women. In fact, migrants make up 10% of the working age population and contribute 10% of GDP.
7b. Immigrants earnings are 13% higher than those of indigenous workers. Dismissed by Statistics Commission for the same reason. Correcting for lower participation rates and higher unemployment among immigrant communities makes average wages across the working age population the same as for the population as a whole.
Annex B
Calculation of tax and NI payments for 2003/4
Personal allowance 2003/4 = 4,615
10% tax band = 1,960 of taxable income
22% tax band = 1,961 to 30,500 of taxable income
40% tax band = above 30,500 of taxable income
(i) Income tax payable on 21,600 income:
10% on 1,960 = 196
22% on 15,025 = 3,305
Total = 3,501
(ii)Employees national insurance = 11% on earnings between 77 and 595 p.w. (4,004 and 30,940 p.a.) = 11% on 17,956 = 1,975.
(iii)Employers national insurance contributions (contracted in) = 12.8% on earnings between 89 and 595 p.w. (4,628 and 30,940 p.a.) and 1% thereafter = 12.8% on 2,172
(iv)Total tax and NI payable on income of 21,600 = 7,648.
Footnotes
| [1] | Home Office press statement in November, 2003, which anticipated a major speech on migration by the Home Secretary, David Blunkett, stating: Effectively managed legal migration is vital to Britain’s economic and social interests, the Home Secretary, David Blunkett, will argue in a speech this evening. Legal migrants make up 8% of the UK’s population but generate 10% of our gross domestic product. The claim was repeated in the House of Lords on 23 Feb 2004 by Baroness Scotland of Asthal who said: Migrants make up 8% of the population but generate 10% of our total wealth. Migrants are substantial net contributors to the Exchequer. |
| [2] | Source LFS – Spring and Autumn 2005. Percentage of children who have UK-born or foreign-born parents are calculated according to birthplace of parent(s) where parents’ birthplace is recorded. Children of one UK-born and one foreign-born parent are allocated 50:50. The percentages have then been applied to the overall child population figures. All figures averaged across Spring and Autumn. |
| [3] | IPPR: Beyond Black and White: Sarah Kyambi |
| [4] | Institute of Fiscal Studies: Immigrants in the British Labour Market: Christian Dustmann and Francesca Fabri. |
| [5] | Home Office Research and Development Stats Paper No. 77 |
| [6] | Employment rate of males aged 16-64 and females aged 16-59 in 2003 – Source ONS Labour Force Survey. The employment rate is currently also 74.7%. |
| [7] | Source ONS. Labour Force Survey: Gross weekly pay in main job 2003. |
| [8] | Commons Written Answer to Andrew Rosindell – 19 April 2006 – Hansard Column 663W. |
| [9] | Source: LFS Summer 2005. |
